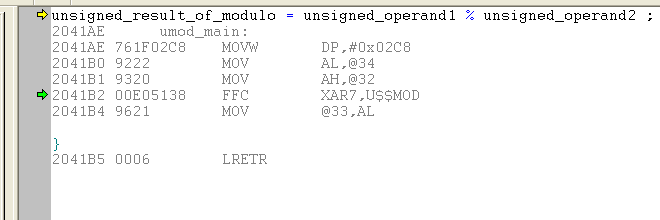
Div In Assembly

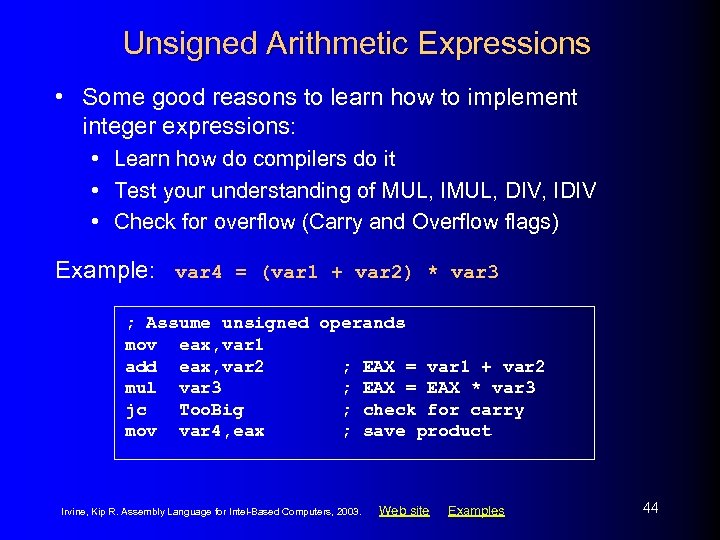
In case of multiplication overflow does not occur because double length registers are used to keep the product.
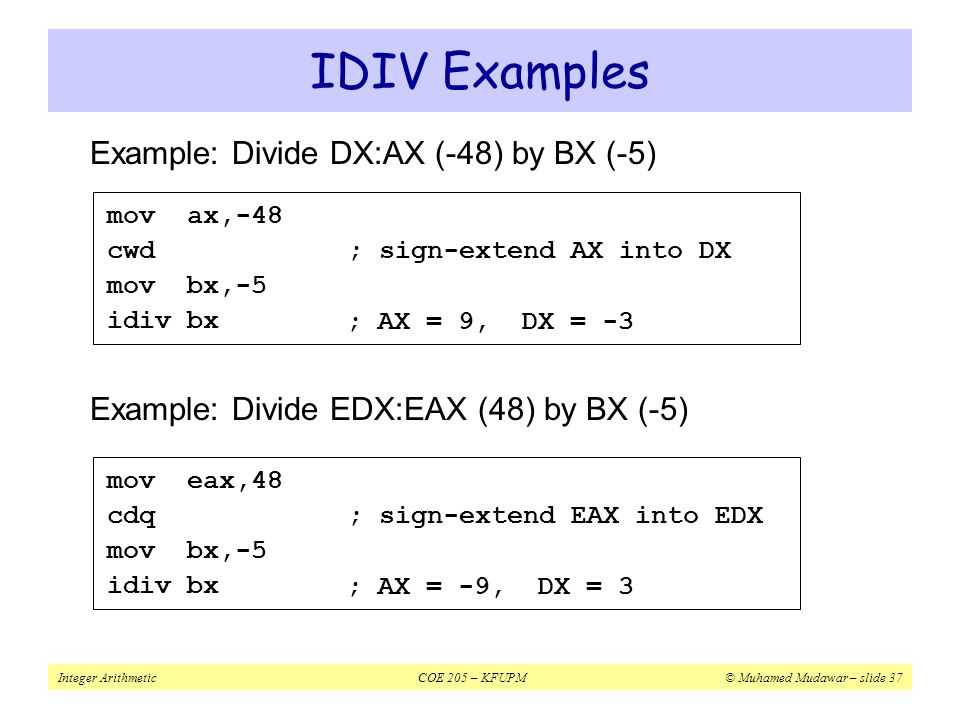
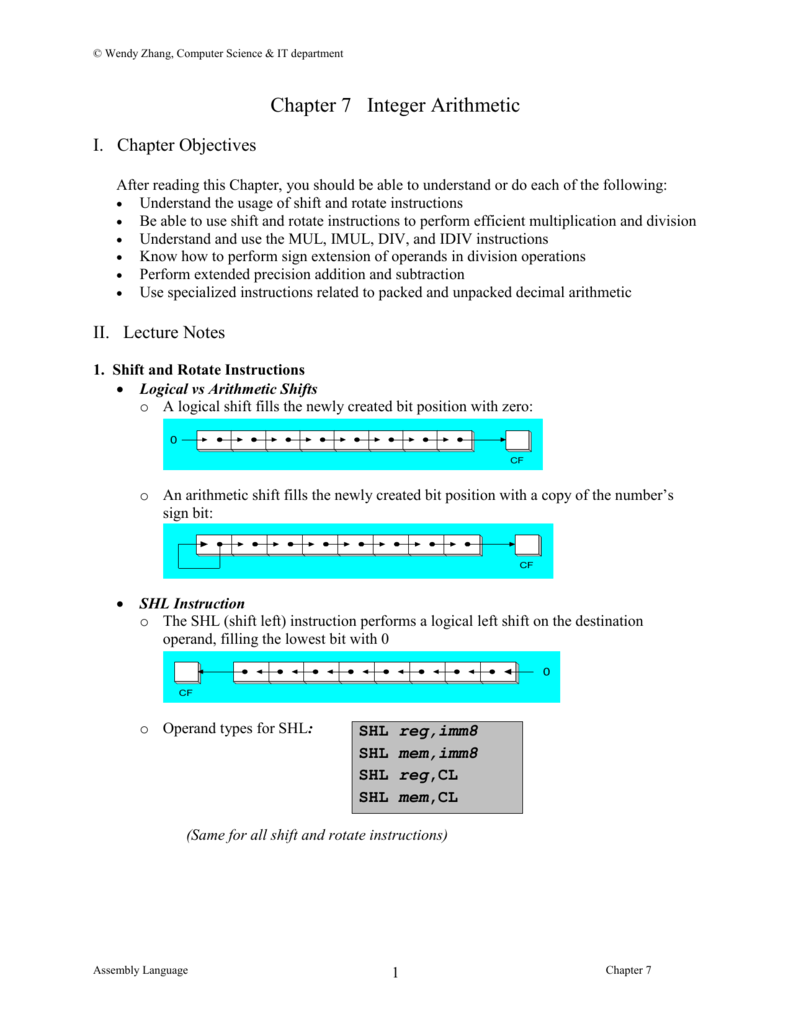
Div in assembly. 8086 has div instruction to perform division. The result of the division is stored in eax and the remainder in edx. Also store result at memory offset 600. Always divides the 64 bits value accross edx eax by a value.
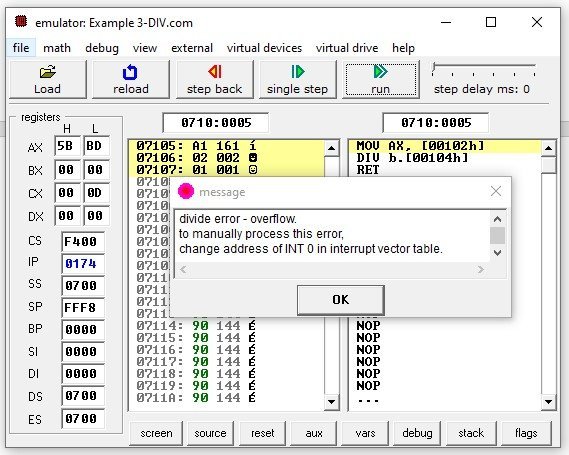
The operation 0x8003 0x100 can be written as follows. There are four division cases depending on the number of bits. Division in assembly language code. The processor generates an interrupt if overflow occurs.
Addition multiplication and division together focus passing values. The div instruction is used to perform a division. The result will be stored. However in case of division overflow may occur.
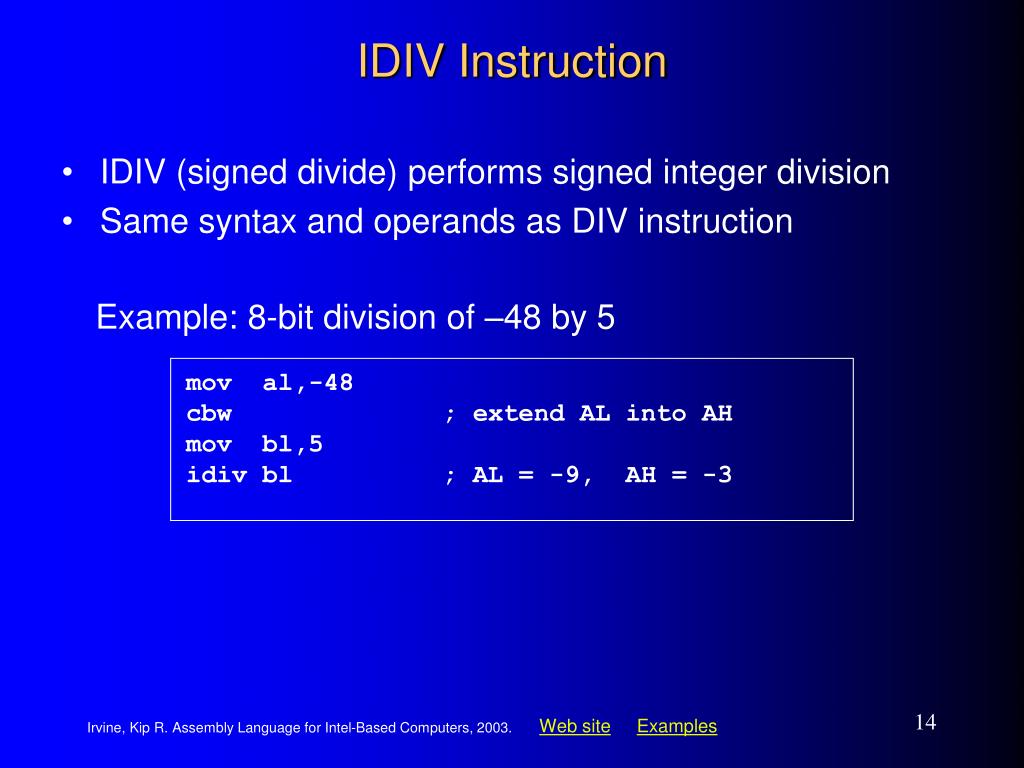
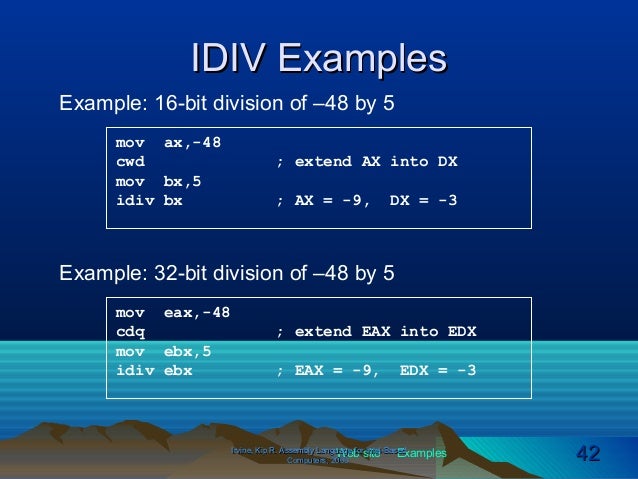
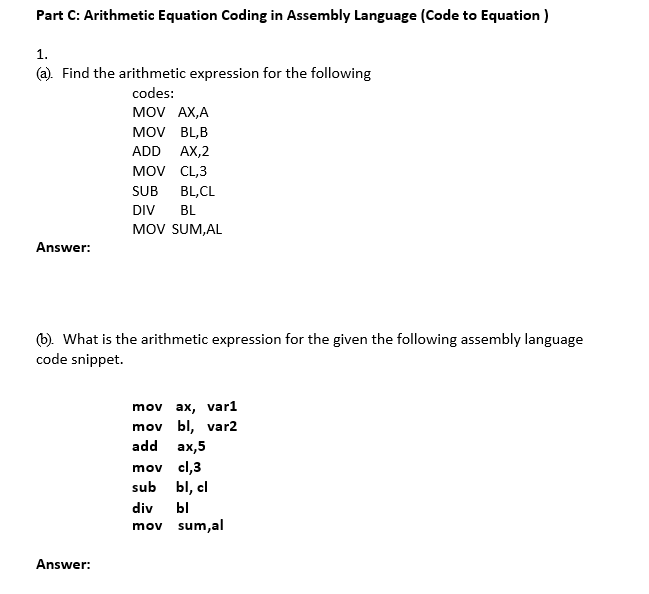
Syntax div value example. Write 8086 assembly language program to divide 16 bit number stored in memory location offset 501. The u means operands and results are in unsigned binary. The denominator resides in a source operand and it should not be immediate.
Divide it with 8 bit number stored in 500h. 3 4 6 2 5 2 25. With n digit integer division there are two results an n digit quotient and an n digit remainder. Take the 8 bit number into bl and 16 bit number into ax.
However it can be register or a memory location. In this video i described how to do division in assembly language so stay tuned with me and subscribe to my channel thank you. Mips uses the hi and lo registers for the results. The size of the divisor 8 16 or 32 bit operand determines the particular register used as the dividend.
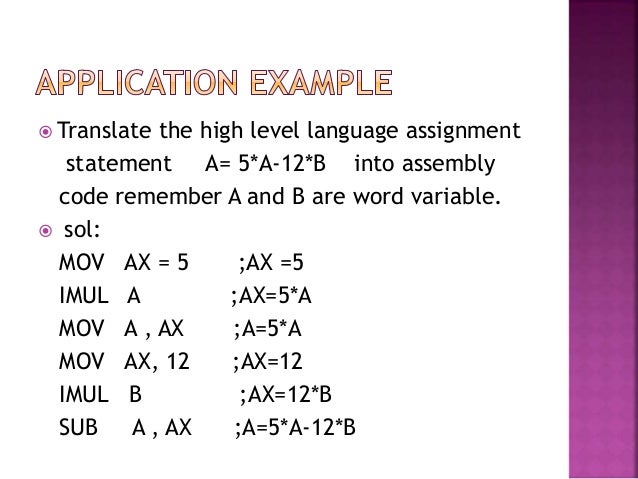
The division operation generates two elements a quotient and a remainder. The quotient is stored in the al ax or eax register respectively. With 32 bit operands there will be in general two 32 bit results. Mov 3 to eax and mov 4 to ebx and use mul ebx to put 12 in eax.
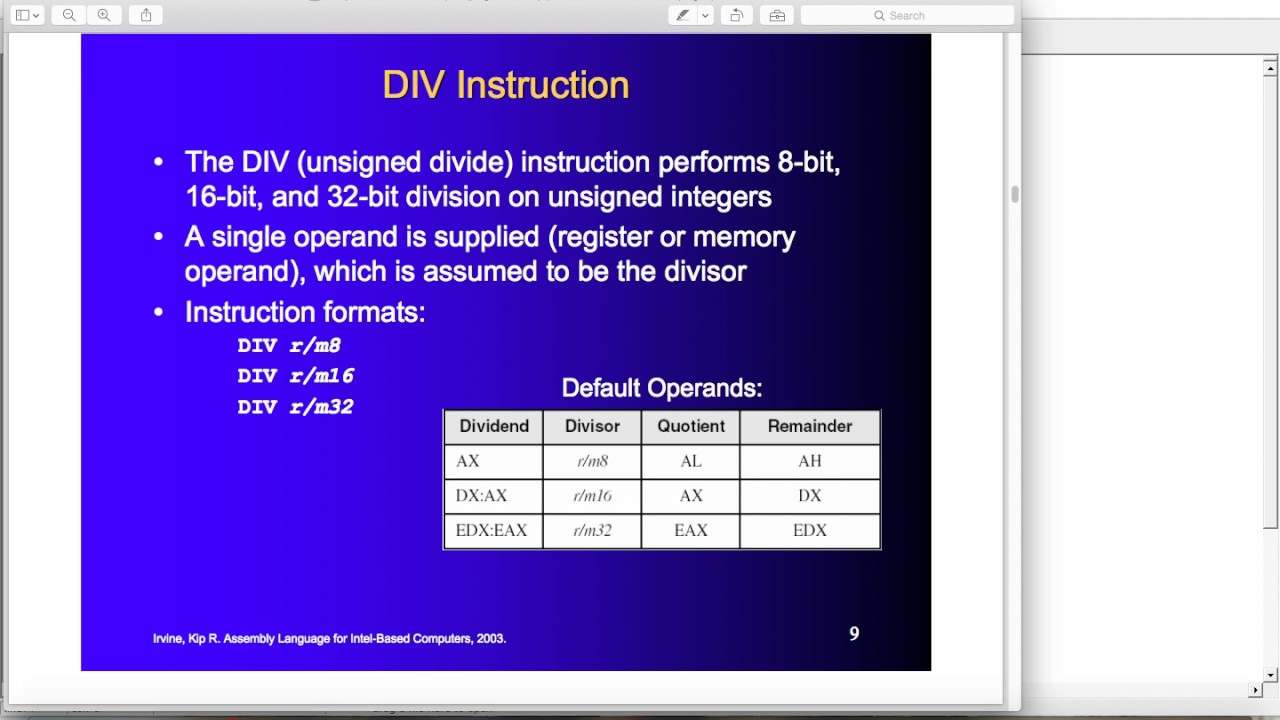
The division can be. The div unsigned divide instruction performs 8 bit 16 bit and 32 bit division on unsigned integers a single operand is supplied register or memory operand which is assumed to be the divisor instruction formats. Now divide ax by bl. Div r m8 div r m16 div r m32.
Divdivides a 16 32 or 64 bit register value dividend by a register or memory byte word or long divisor.